The spinal cord is much shorter than the vertebral column ending at a vertebral level of. The two grooves are named as follows.
10 Surprising Facts About The Spinal Cord Sapna Pain Management Blog
The spinal cord contains is located inside the vertebral canal which is formed by vertebrae CNS has two types of tissue.

. The spinal cord begins at the foramen magnum where it is continuous with the medulla oblongata. The spinal dura mater attaches to the tectorial membrane and posterior longitudinal ligament superiorly. The Spinal cord begins from the medulla oblongata which is at the bottom of the brain stem and View the full answer.
It is elongated cylindrical suspended in the vertebral canal and protected by vertebrae Surrounded by the meninges and cerebrospinal fluid CSF. These are peripheral nerves or those that run through other parts of the body and transmit message to and from the brainspinal cord. It extends from the medulla to the superior border of L2.
The spinal cord is a nervous system structure dedicated to relaying information from the periphery to the brain and back as well as carrying out certain levels of integration such as those found in many reflexes. The spinal cord extends from the foramen magnum where it is continuous with the medulla to the level of the first or second lumbar vertebrae. It is covered by the three membranes of the CNS ie the dura mater arachnoid and the.
The dura mater of the spinal cord differs from that of the brain by having only one layer. It is a vital link between the. The spine is made up of vertebrae back bones that protect and surround the spinal cord which is a column of nerve tissue.
The spinal cord is roughly cylindrical but slightly flattened anterior posterior. It carries signals between the brain and the. Whereas the brain develops into a complex series of nuclei and fiber tracts the spinal cord remains relatively simple in its configuration Figure 1612.
The arrangement of gray and white matterin the spinal cordis relativelysimple. Origin and terminus of Spinal cord. The cranial nerves connect the head and neck directly to the brain but the spinal cord receives sensory input and sends motor commands out to the body through the spinal nerves.
The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system CNS. The Internal Anatomy of the Spinal Cord. 100 3 ratings Answer- Spinal cord lies in vertebral canal.
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system CNS. Describe the gross external anatomy of the spinal cord. The primary function of spinal cord is a transmission of.
Describe the anatomy of the spinal cord by completing the following chart. Anatomy of the Spinal Cord. White mater is arranged in tracts around the gray mater.
The blood vessels which carry oxygen to the spinal cord also use these spaces. Your spinal cord is one of the main parts of your nervous system. How Does The Spinal Cord Work University Of Iowa Hospitals Clinics Gross Morphology Of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe What Is The Difference Between The Spinal Cord And A Spinal Nerve Quora Describe of the wallpaper.
2It contains cervical and lumbar enlargements that serve as. View the full answer. SPINAL CORD The main pathway for information connecting the brain and peripheral nervous system.
It is situated inside the. Describe the functional anatomy of the spinal cord using the follA case of Spinal Cord Injury owing terms. The structure of the spinal cord aids it in carrying out these relaying and integrative functions.
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system CNS which extends caudally andis protected by the bony structures of the vertebral column. Anatomy Of Spinal Cord Khaleel Alyahya Phd Med King Saud University Ppt Download. Your spinal cord is a cylindrical structure that runs through the center of your spine from your brainstem to your low back.
The cerebrum the diencephalon the. Its a delicate structure that contains nerve bundles and cells that carry messages from your brain to the rest of your body. The spinal cord contains white matter gray matter tracts roots and spinal nerves.
Describe the anatomy of the spinal cord. The brain and the spinal cord are the central nervous system and they represent the main organs of the nervous system. Up to 24 cash back Cross-sectional anatomy of the spinal cord The spinal cord appears to be somewhat flat with two grooves that mark its surface.
The internal anatomy of the spinal cord is quite complex. White matter consists of bundles of nerve fibers called axons. White matter and gray matter.
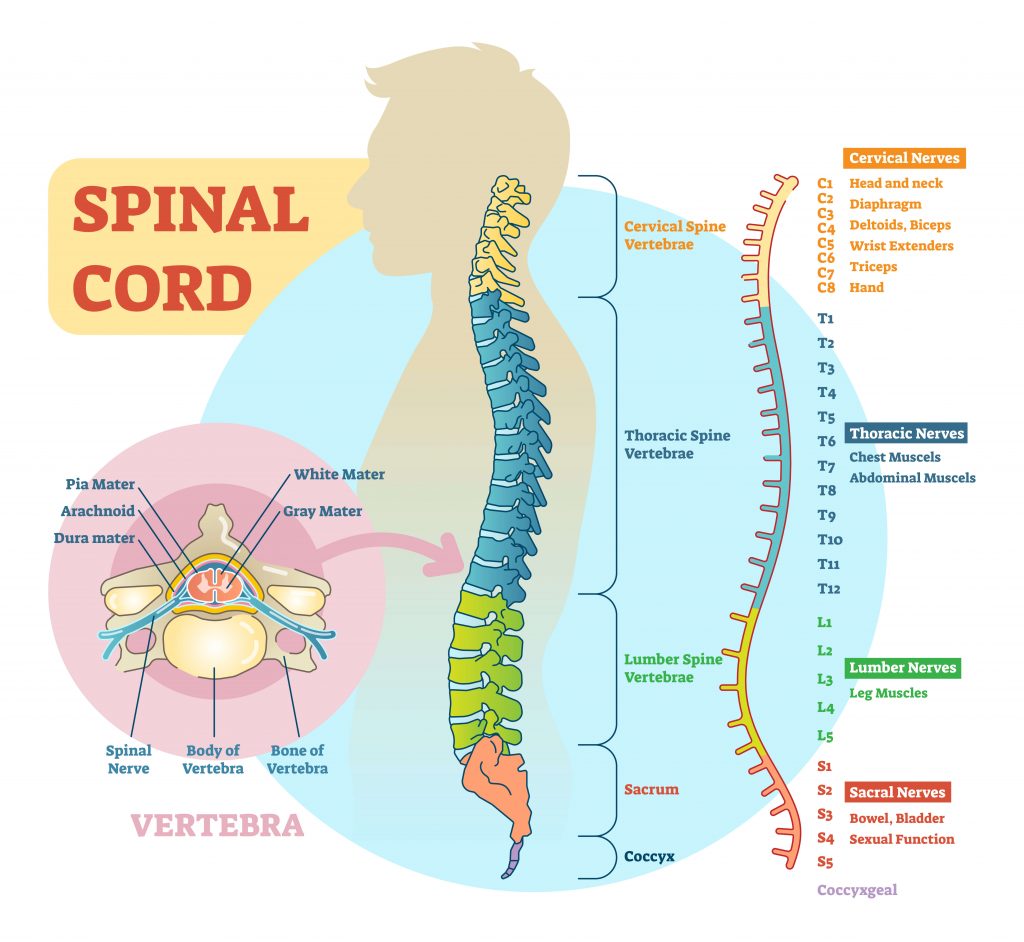
3 points of associated segmentsspinal nerve pairs Spinal cord Cervical region Thoracic region Lumbar region Sacral. The spinal nerves enter and exit the spinal cord through small spaces between the vertebrae. You have 8 pairs of cervical nerves 12 thoracic 5 lumbar and 6 sacral.
The ventral anterior median fissure and the more shallow dorsal posterior median sulcus. 1The spinal cord begins as a continuation of the medulla oblongata and terminates at about the second lumbar vertebrae in an adult. In transversesections the gray matter is conventionally divided into dorsalposterior lateraland ventralanterior horns.
The spinal cord is a long thin tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the medulla oblongata of the brain to the level of the lumbar region. The spinal cord is a bundle of spinal nerves wrapped together. White matter has bundles of nerve fibers or axons that run up.
The spinal cord is a single structure whereas the adult brain is described in terms of four major regions. The spinal cord is a continuation of the Central Nervous System CNS which comprises the brain and the spinal cord. The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system CNS located within the spinal canal of the vertebral column.
It extends from foramen magnum where it is continuous with medulla o. It consists of axons that transmit impulses to and from the brain or between levels of gray mater within the spinal cord. The length ranges from 42 - 45 cm and is approximately 2 cm in diameter.
The spinal cord is a long bundle of nerves and cells that extends from the lower portion of the brain to the lower back. Spinal nerves branch out from the spinal cord. The periosteal layer is missing because the vertebral canal unlike the skull has its own true periosteum.
The bundles of fibers connected to the CNS are called tracts. The interior of the cord is formed by gray matter which is surrounded bywhite matter Figure 111A. To keep things simple the center of the cord consists of gray mater.
The spinal cord is the most important structure between the body and the brain. White matter gray matter tracts roots and spinal nerves. They run up and down the length of the spinal cord allowing different levels of the CNS to communicate.
3 rows Anatomy.

Anatomy Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord And Nerves Youtube

0 Comments